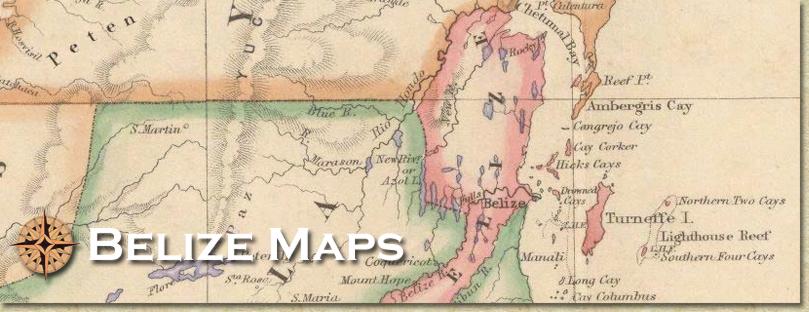
Maps of San Pedro and Ambergris Caye > Geologic resources of Belize Geologic resources in briefThe geological resources of Belize include oil, clays, barite, sand and gravel, granite, gypsum, quartz sand, dolomite and limestone. There are indications that Belize may have deposits of molybdenum in the Maya Mountains. Sites with high quality silica deposits have been identified. A few rubies are said to have been discovered in the south of the country during colonial times. Oil has been extracted from the Spanish Lookout Reservoir since 2006. This oil is located at a depth of 3,000 feet. Between 1999 and 2008, 2,300 ounces of gold were extracted from the Ceibo Chico area of the Maya Mountains by a Belizean company. The other area with gold potential is the mountain watersheds adjacent to the Sittee River and the Raspaculo branch of the Macal River. The Geology of BelizeThe geology of Belize can be divided broadly into the Northern Lowlands, the Maya Mountains, the Toledo Beds and the Pliestocene deposits, but there are other features including volcanic deposits of bentonite in the north and volcanic outcrops along the southern boundary of the Maya Mountains. The Northern Lowlands The northern lowlands are made up of heterogeneous limestone sediments which are referred to as the Yucatan Platform. The first deposition of limestone was around 200 million years ago and the second period was around 50 million years ago when most of the land in the country was submerged in a shallow sea. The Maya Mountains South and west of the country are the Maya Mountains. These mountains are the most impressive geological feature in the country and are composed of volcanic and sedimentary rocks that have become metamorphosed or chemically altered. The oldest rocks in the Maya Mountains are granites that occur at the Mountain Pine Ridge. These granites were formed when magma cooled below the earth’s surface about 360 millions of years ago. The second oldest rocks in Belize and the Maya Mountains comprise the Santa Rosa Metasediments which were formed about 330 million years ago. Pliestocene Alluvium Deposits To the east and north of the Maya Mountains are the Pleistocene alluvium deposits of the coastal areas. These infertile deposits were washed down from the Maya Mountains less than a million years ago. Toledo Beds In the southern areas of the Toledo district, gravels, sands and muds dominate the geology. These are called the Toledo Beds and consist mainly of thin bedded shales and mudstones, with some blue calcareous (calcium derived) sandstones and patches of limestone. |
 |
Maps of Belize and Ambergris Caye |
 |

|
